Mission statement
We develop and support open-source, "big data"–enabled AI analysis tools designed to be accessible to biology researchers without extensive computational expertise. Our group is fully committed to FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) principles in all aspects of our software development. We engage with the national community to develop, support, and disseminate novel technologies of benefit to all.
All code is available here: https://github.com/EpiGenomicsCode
Infrastructure development
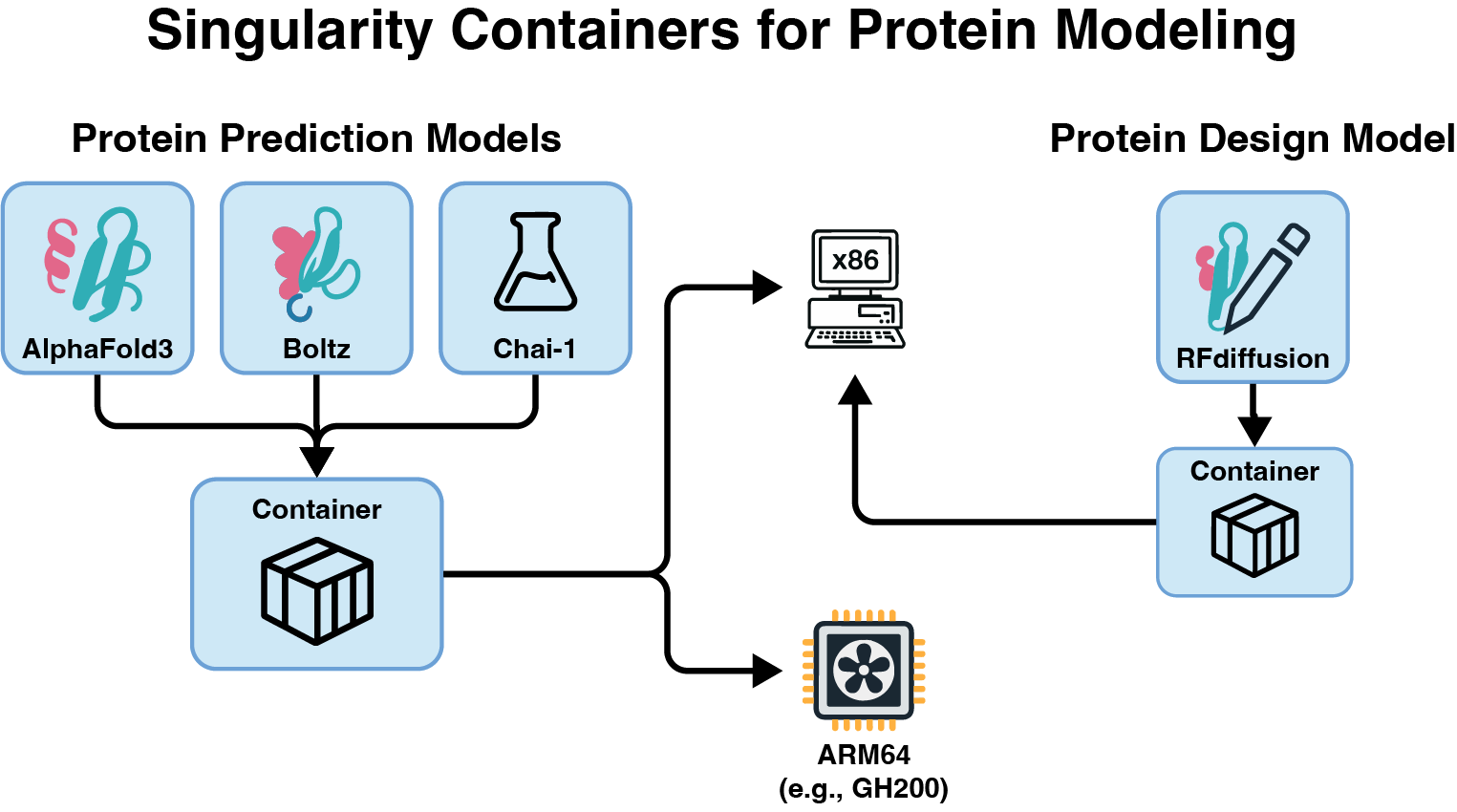
We build scalable, reproducible, and FAIR-aligned platforms to support domain specific computation and analysis. We recently developed a high-throughput containerized solution for large-scale protein structure modeling and design. These containers are architected to make efficient use of available GPU and CPU resources. Our focus on interoperability and accessibility is echoed in our ScriptManager platform which provides an interactive genomics analysis environment which abstracts away underlying compute complexity and fosters reproducible FAIR workflows for users of varied computational literacy. Attempting to address the reproducibility crisis in genomics, we developed GenoPipe to peform genotype of origin detection from (epi)genomic datasets. Focusing on methodological robustness, we also developed the Adversarial Robustness and Explainability framework to provide explainable, adversarial resistant validation checks into machine learning pipelines. This helps to promoting trustworthy, reproducible model evaluation that aligns with FAIR principles by documenting provenance and interpretability features.
Highlights
-
Protein structure prediction and design for high-throughput computing.
Mathew VS, Kellogg GD, Lai WKM.
bioArxiv 2025, https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.07.18.665594 -
Adversarial Robustness and Explainability of Machine Learning Models.
Gafur J, Goddard S, Lai WKM.
Practice and Experience in Advanced Research Computing 2024, https://doi.org/10.1145/3626203.3670522 -
GenoPipe: identifying the genotype of origin within (epi)genomic datasets.
Lang O, Srivastava D, Pugh BF, Lai WKM.
Nucleic Acids Research 2023, 51 (22), 12054-12068. PMID: 37933851; PMCID: PMC10711449. -
ScriptManager: an interactive platform for reducing barriers to genomics analysis.
Lang O, Pugh BF, Lai WKM Lai WKM.
Practice and Experience in Advanced Research Computing 2022, https://doi.org/10.1145/3491418.3535161 -
ArchTEx: accurate extraction and visualization of next-generation sequence data.
Lai WKM, Bard JE, Buck MJ.
Bioinformatics 2012, 1;28(7):1021-3. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts063. PMID: 22302569.
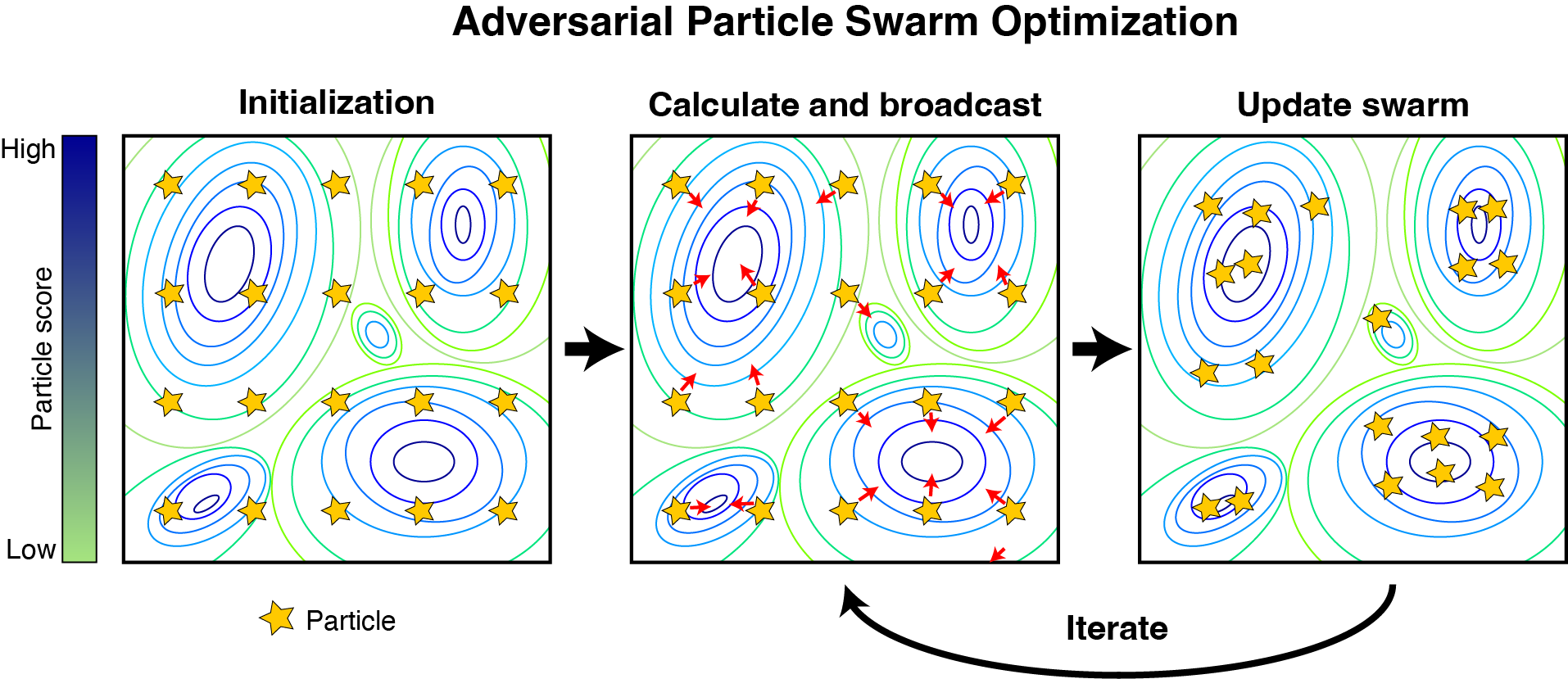
Gateway development
Current genomic projects generate hundreds of terabytes of sequencing data and associated metadata, which require sophisticated management for effective tracking, analysis, and visualization. To meet these challenges, we developed the STENCIL platform. It visualizes results of integrated Galaxy workflows while providing interactive analysis tools for further exploration. STENCIL has proven essential for interpreting complex datasets, enabling biochemists with minimal genomics training to readily understand experimental results. In alignment with the NIH’s emphasis on experimental rigor and reproducibility, we also use and develop the PEGR platform to track detailed metadata on experimental procedures as they occur. PEGR captures comprehensive information for each experiment—including enzyme catalog numbers and sample identifiers—in real time, embedding this metadata in a searchable interface directly linked to the resulting sequencing data, the Galaxy platform, and STENCIL. This workflow supports fully reproducible bioinformatics that can be traced back to the original experimental design.
Highlights
-
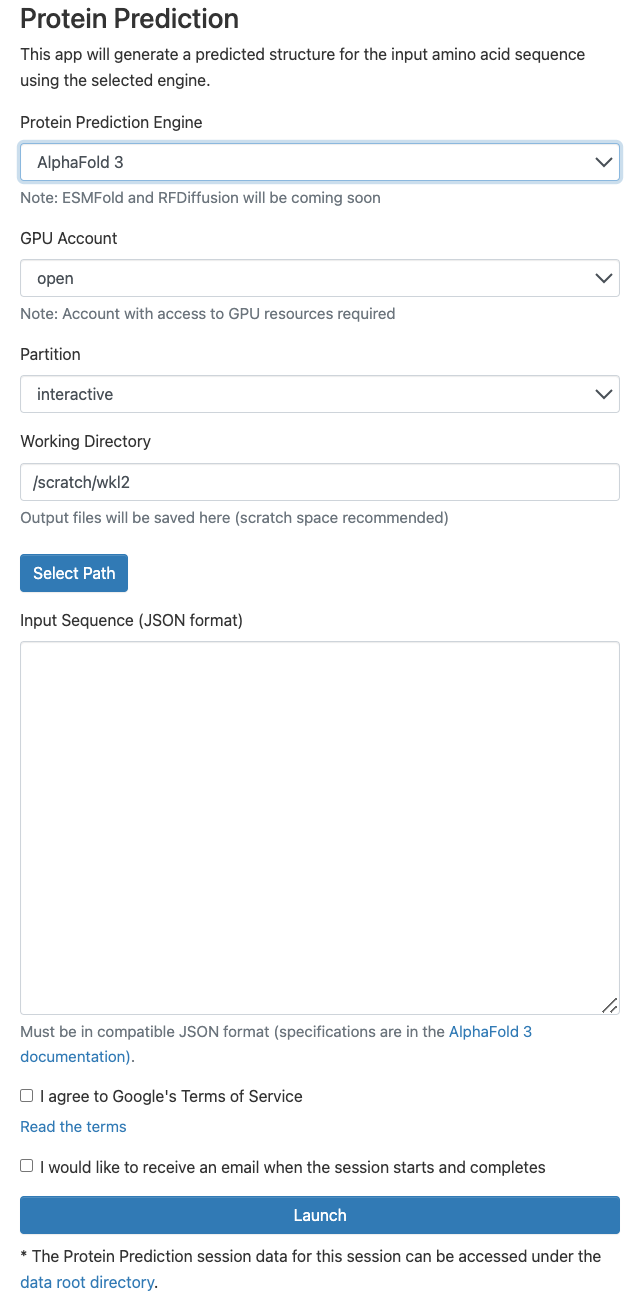
AlphaFold accessibility: an optimized open-source OOD app for Protein Structure Prediction.
Mathew VS, Hansen M, Lai WKM
GOOD25 Conference - Harvard -
PEGR: a flexible management platform for reproducible epigenomic and genomic research.
Shao D, Kellogg G, Nematbakhsh A, Kuntala PK, Mahony S, Pugh BF, Lai WKM.
Genome Biology 2022, 19;23(1):99. PMID: 35440038 PMCID: PMC9016988 -
STENCIL: A web templating engine for visualizing and sharing life science datasets.
Sun Q, Nematbakhsh A, Kuntala PK, Kellogg G, Pugh BF, Lai WKM.
PLoS Computational Biology 2022, 9;18(2):e1009859. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009859. PMID: 35139076; PMCID: PMC8863220.